Leg length discrepancies can be categorized into two types: Structural Discrepancy and Functional Discrepancy.
Leg length discrepancies can be categorized into two types: Structural Discrepancy and Functional Discrepancy.
In structural discrepancy, the bones of both legs are physically different in length.
In functional discrepancy, the bone lengths are equal, but other issues, such as problems with the foot, ankle, knee, hip, or pelvis, may cause the legs to become asymmetrical.
Around 33% of all people have legs with small length differences. Because the difference is so small, it’s usually not noticeable and doesn’t cause any problems that require treatment.

Large leg length discrepancies, on the other hand, can cause difficulty in all manner of movement.
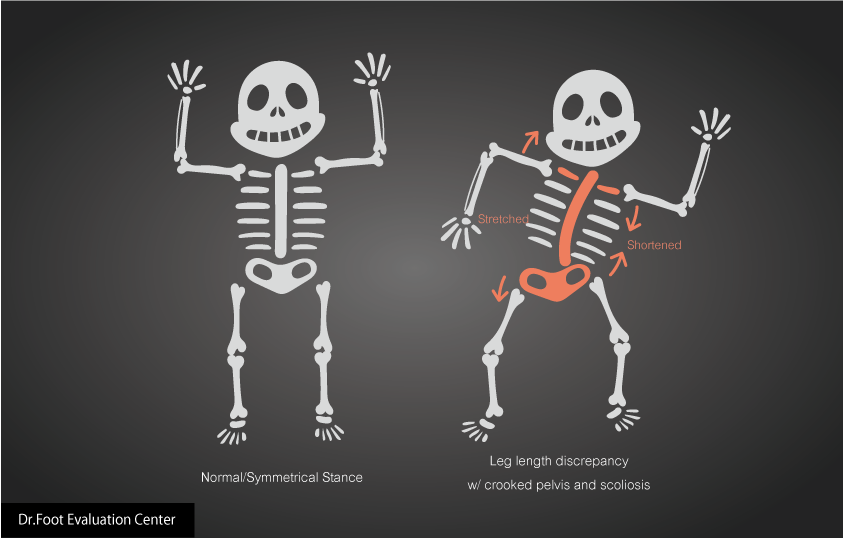
Leg length discrepancy can appear as early as birth or occur over time as the child develops, but the issue is usually left unnoticed until the child begins to crawl or walk. The leg length discrepancy can cause an abnormal gait and weight distribution on the feet. Leg length discrepancy may also lead to uneven bone sizes, walking difficulties, fatigue, or other issues.
CAUSES
Leg length discrepancy can be an issue that occurs at birth or a problem that develops over time due to illnesses or injuries. In the case of the latter, broken leg bones are most likely to cause leg length discrepancy, especially if it occurs during childhood years where the bones may grow faster than the broken bone may recover.
Bone infection or diseases such as neurofibromatosis can also cause leg length discrepancy.
POTENTIAL PROBLEMS
Even if the length between both legs may not be visually different, even a small physical difference may cause a large biomechanical difference. In order to compensate for the discrepancy, the body may change, such as causing the pelvic bone to tilt or leading to a functional scoliosis. A leg length difference of 2 cm would be enough to cause the longer leg to carry more weight for longer periods of time than the shorter leg, which is known as gait asymmetry. Gait asymmetry, if left untreated, may increase the risk of hip or knee osteoarthritis over time.

A difference of 3.5% to 4% in total leg length would usually show minor problems, such as limping or difficulty walking, which in turn would cause fatigue from the extra effort needed to walk.

TREATMENT
So how can you fix leg length discrepancy? While surgery is an option, it is a costly and irreversible process, and may cause stress and other discomforts during treatment. Our insoles and shoes can be custom-tailored to suit your needs, compensating for any leg length discrepancy and enabling you to walk with a normal and comfortable gait!
